You’ve probably noticed a few new cars driving on the road lately. They have a modern, sleek look to them. EV cars are becoming increasingly popular for their cost-effectiveness and for reducing their environmental impact.

Gas vs. EV
Many are hesitant about the upfront costs of EVs, but they are more cost-effective than gasoline vehicles. Charging an electric car is cheaper than filling up gas. According to AAA, the average U.S. cost is $3.50 per gallon, whereas the comparable cost for EV charging is $1.41. The cost of gas prices is constantly in flux and increased 41% in July 2022 at $4.67. But electrical costs remain steadier because a state’s public utility commission manages them. Renewable energy prices have also declined in the past years. Furthermore, EVs require less regular maintenance than gas-powered vehicles because they have fewer parts.
EV Charging stations
Where am I supposed to charge my EV? There are fewer EV charging stations than gas stations, but they are increasing. Luckily the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) created new energy incentives, such as the EV charging station tax credit, to increase the number of stations.
Clean Vehicle Tax Credit
You can also receive a clean vehicle tax credit for purchasing an electric vehicle. The credit is worth $2,500 to $7,500 for new EVs (depending on requirements). The new credit now includes used EVs, accommodating cheaper options. The credit offers up to $4,000, limited to 30% of the sale price for used EVs. To read more on the EV charging tax credit, click here.
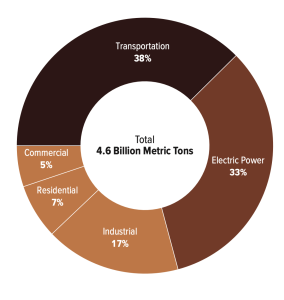
ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT
Driving an electric vehicle instead of a gas-powered vehicle helps reduce emissions. Transport accounted for 38% of US carbon dioxide emissions in 2021. High emissions pollute the environment and contribute to health problems, smog, and global warming. Switching to an EV can reduce your carbon footprint.
The amount of emission your EV produces depends on the source of electricity. If your electricity come from traditional energy sources like coal and natural gas, your EV will still produce emissions. If it comes from a renewable energy source, your EV will have significantly less emissions. If we take a look at the life cycle assessment for EVs vs. gas cars. This includes material extraction, manufacturing, distribution, use of product, reuse/ recycling, disposal. EVs are reported to emit a third of the gas powered emissions in a life cycle assessment. The gap between emissions is predicted to increase in coming years with EVs using greener electric sources and tech.

~By Camryn Iftiger, Intern at Seed solar, Electric, and Engineering. Camryn is a 2021 graduate from UVM with a major in Environmental Studies and English.
